#
Dutree
title: Install dutree label: Install dutree order: 100 authors:
- name: Charl Cronje email: charl@webally.co.za link: https://blog.webally.co.za avatar: https://assets.webally.co.za/avatars/darker.jpg edit: repo: "https://github.com/charlpcronje/setup.docs.devserv.me/edit/" base: /src branch: main label: Edit on GitHub editor: enabled: false favicon: favicon.png links:
- text: Projects Portfolio link: https://webally.co.za/projects
- text: Wiki, Tips and Docs link: https://docs.webally.co.zao.za
- text: Resume link: https://cv.webally.co.za
- text: LinkedIn link: https://www.linkedin.com/in/charlpcronje
- text: GitHub link: https://github.com/charlpcronje
- text: Upwork Profile link: https://www.upwork.com/freelancers/~01ccb1439024ec9c50 footer: copyright: "webAlly © Copyright . All rights reserved."---
dutree – A CLI Tool to Analyze Disk Usage in Coloured Output
dutree is a free open-source, fast command-line tool for analyzing disk usage, written in Rust programming language. It is developed from durep (disk usage reporter) and tree (list directory content in tree-like format) command line tools. dutree therefore reports disk usage in a tree-like format.
It displays coloured output, depending on values configured in the GNU LS_COLORS environment variable. This env variable enables for setting the colours of files based on extension, permissions as well as file type.
#
dutree Features:
- Show the file system tree.
- Supports aggregating of small files.
- Allows for comparing different directories.
- Supports excluding of files or directories.
#
How to Install dutree in Linux Systems
To install dutree in Linux distributions, you must have rust programming language installed on your system as shown.
sudo curl https://sh.rustup.rs -sSf | shOnce rust installed, you can run the following command to install strong>dutree in Linux distributions as shown.
cargo install --git https://github.com/nachoparker/dutree.gitAfter installing dutree, it uses environment colors according to the variable LS_COLORS, it has the same colors ls --color command that our distro has configured.
ls --colorThe simplest way of running dutree is without arguments, this way it shows a filesystem tree.
dutree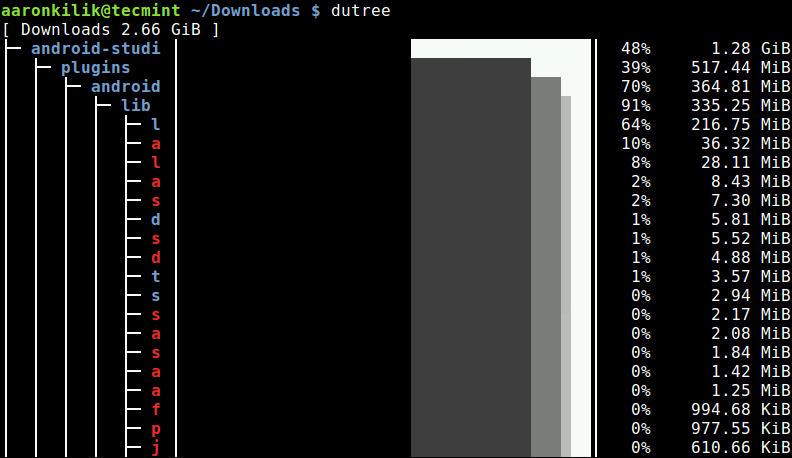
To display real disk usage instead of file size, use the -u flag.
dutree -u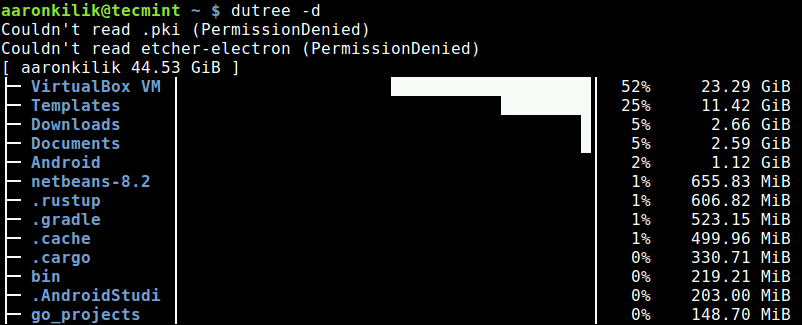
#
Show Directories in Depth
You can show directories up to a given depth (default 1), using the -d flag. The command below will show directories up to a depth of 3, under the current working directory.
For example if the current working directory (~/), then display size of ~/*/*/* as shown in the following sample screenshot.
dutree -d 3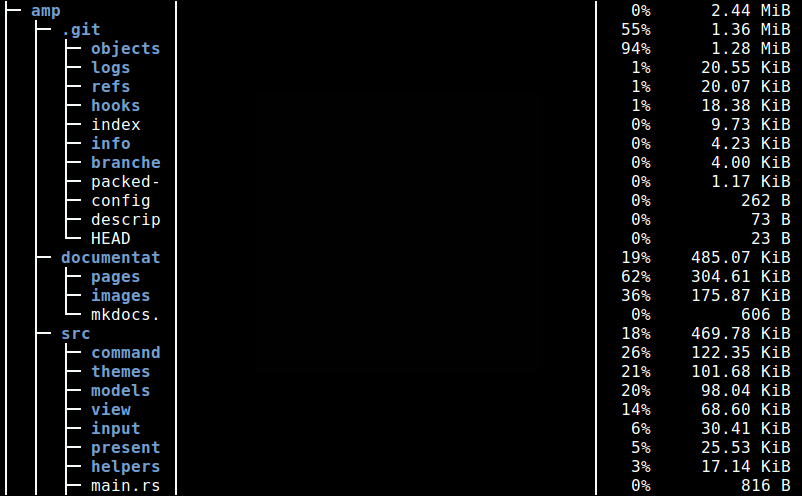
#
Exclude Files or Directories in Output
To exclude matching a file or directory name, use the -x flag.
dutree -x CentOS-7.0-1406-x86_64-DVD.iso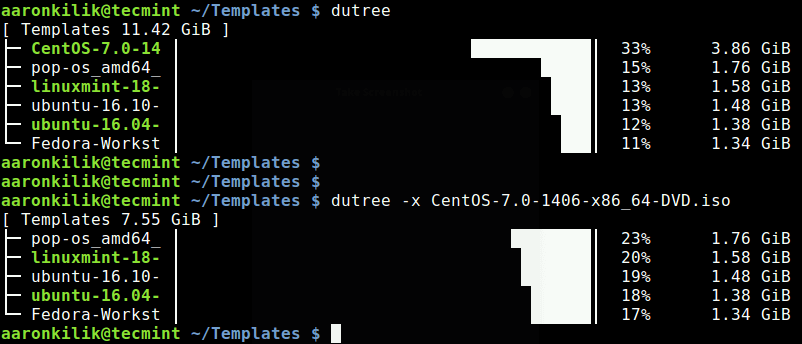
You can also get a quick local overview by skipping directories, using the -f option, like so.
dutree -f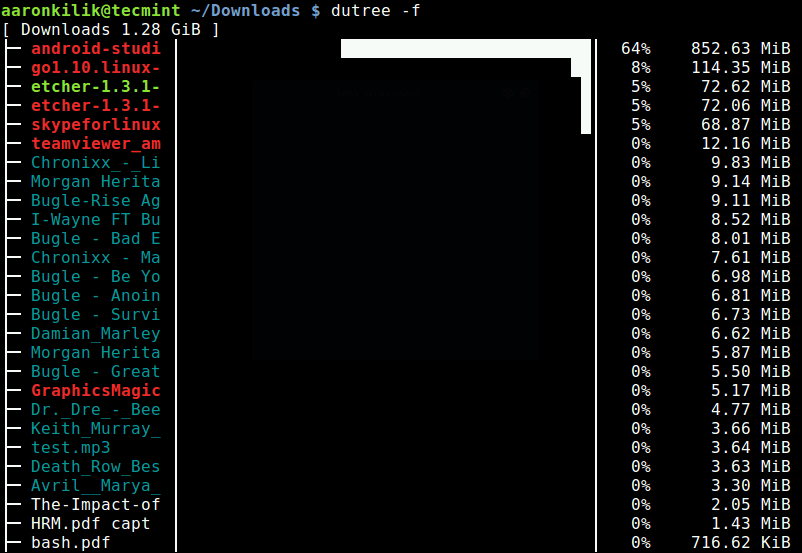
A full summary/overview can be generated using the -s flag as shown.
dutree -s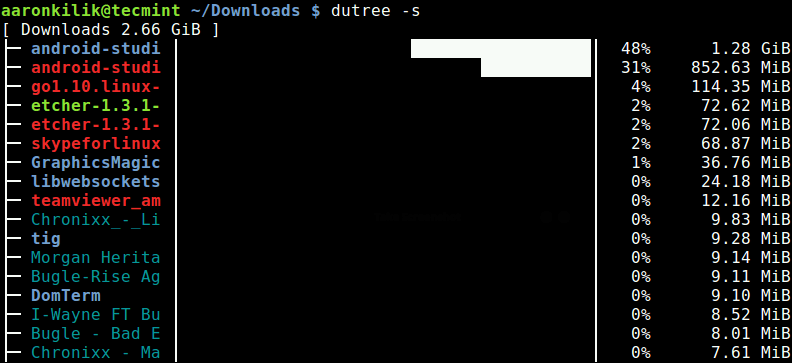
#
ggregate Small Files
It is possible to aggregate files smaller than a certain size, default is 1M as shown.
dutree -a
The -H switch allows for excluding hidden files in the output.
dutree -HThe -b option is used to print sizes in bytes, instead of kilobytes (default).
dutree -bTo turn off colors, and only display ASCII characters, use the -A flag like so.
dutree -AYou can view the dutree help message using the -h option.
dutree -h
Usage: dutree [options] [..]
Options:
-d, --depth [DEPTH] show directories up to depth N (def 1)
-a, --aggr [N[KMG]] aggregate smaller than N B/KiB/MiB/GiB (def 1M)
-s, --summary equivalent to -da, or -d1 -a1M
-u, --usage report real disk usage instead of file size
-b, --bytes print sizes in bytes
-x, --exclude NAME exclude matching files or directories
-H, --no-hidden exclude hidden files
-A, --ascii ASCII characters only, no colors
-h, --help show help
-v, --version print version number- dutree Github Repository: https://github.com/nachoparker/dutree
- dutree is a simple yet powerful command-line tool to show file size and analyze disk usage in tree-like format, on Linux systems. Use the comment form below to share your thoughts or queries about it, with us.